Chosen theme: Case Studies on Successful Warehouse Automation Implementations. Explore inspiring, real-world transformations where data, design, and teamwork turned bottlenecks into flow. Learn what worked, why it worked, and how you can adapt proven approaches to your operation. Subscribe and share your challenges—we’ll tailor future case deep-dives to your questions.

What Success Looks Like: Metrics That Matter
High-impact teams captured pre-automation benchmarks—pick rates, order cycle times, dock-to-stock hours, and error percentages—then targeted realistic, incremental improvements. The best results came from weekly KPI reviews, fast experiment cycles, and the discipline to sunset ideas that did not move the needle.
Technology Combinations Behind the Wins
One distributor layered autonomous mobile robots beneath existing shelving and added pick-to-light prompts at hotspots. This hybrid approach cut walking distances, simplified training, and avoided major construction. Crucially, it respected brownfield constraints while still delivering significant throughput gains and faster associate onboarding.
Technology Combinations Behind the Wins
A retailer implemented a shuttle-based AS/RS to buffer inventory close to pack-out. During peak weeks, the system dynamically balanced loads across aisles, feeding work evenly. Instead of hiring seasonal labor at scale, they flexed capacity through software-controlled waves and smarter slotting strategies.
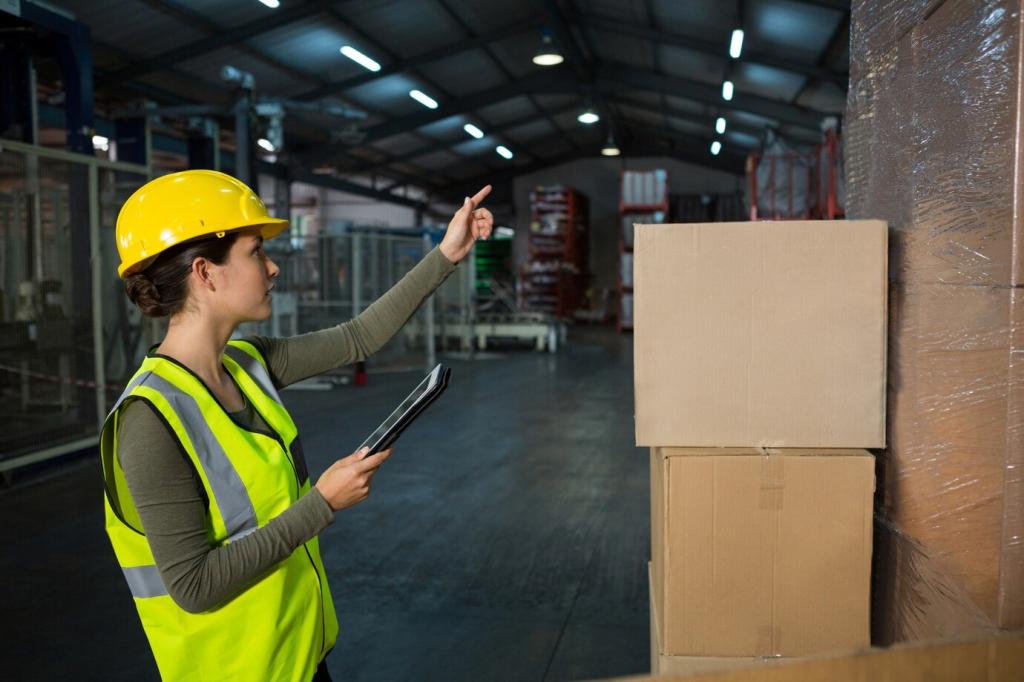


People at the Center: Change Management That Worked
In multiple case studies, seasoned forklift operators became AMR champions after hands-on workshops. Their practical instincts improved traffic rules, zone handoffs, and charging routines. With their input, the fleet behaved predictably on busy days, lowering stress while elevating pride in the operation’s performance.
People at the Center: Change Management That Worked
Leaders who shared timelines, risks, and decision criteria early earned credibility. Daily standups during pilots created a safe forum for concerns. Associates saw their feedback implemented within days, which transformed skepticism into advocacy and kept the project resilient when inevitable hiccups appeared under real load.
People at the Center: Change Management That Worked
Rather than treating safety as a checklist, teams embedded it into design narratives: clear line markings, bright visual cues, speed zones, and audible alerts. Incident drills during pilots built muscle memory. The result was fewer near-misses, calmer aisles, and confidence that growth would not compromise wellbeing.
Phased Rollouts, Not Big Bangs
One operation ran a ninety-day pilot in a single zone with well-instrumented metrics. After confirming stability and net throughput gains, they expanded to adjacent zones. This created a momentum engine—each phase funded the next, preserving cash while steadily reducing operational risk and uncertainty.
Phased Rollouts, Not Big Bangs
Several teams executed dual-running periods where legacy and automated flows processed the same orders. This exposed edge cases, mismatched master data, and timing conflicts. By resolving issues before full cutover, they avoided service disruptions and kept customer promises intact during the most delicate transition window.
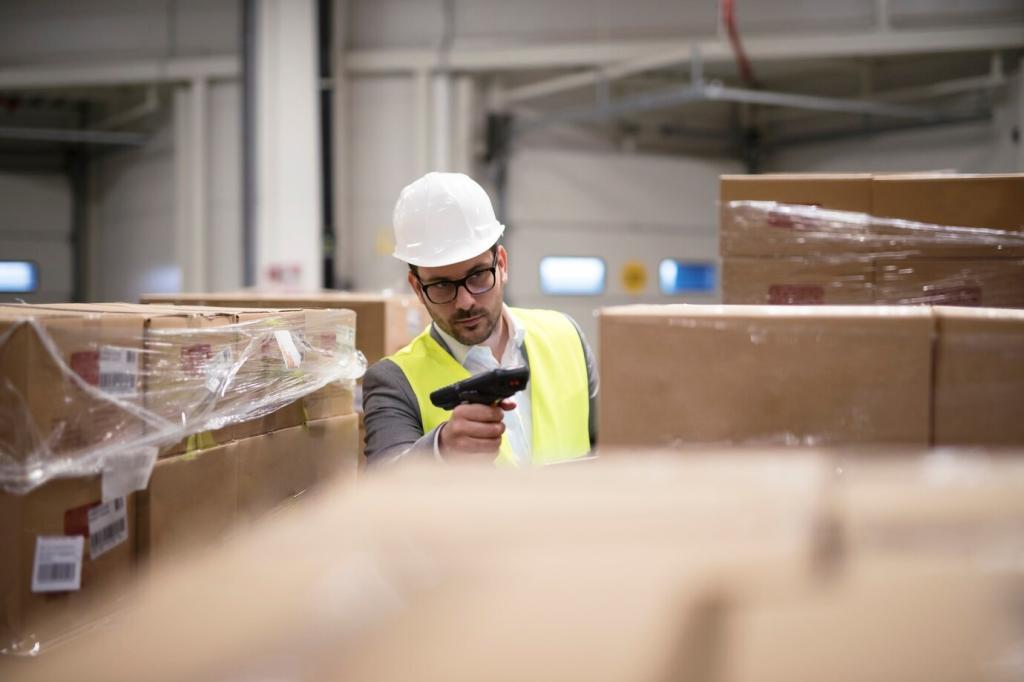

Cost, ROI, and the Payback Story
High performers modeled software subscriptions, spare parts, training, IT overhead, and process redesign alongside hardware. They compared options with scenario analysis, asking, “What if volumes shift or SKUs proliferate?” This full-picture approach prevented budget shocks and ensured the solution could evolve gracefully with demand.
Cost, ROI, and the Payback Story
Across cases, payback improved when pilots targeted clear bottlenecks and avoided over-automation. Phased investments delivered returns sooner, funding subsequent stages. Teams also captured soft savings—fewer chargebacks, less overtime volatility, and improved retention—while still grounding models in conservative, verifiable operational metrics and assumptions.
Data as the Flywheel
Digital Twins that Earn Their Keep
Teams validated aisle widths, charging locations, and buffer sizes with simulation before committing. After go-live, they updated the twin with real telemetry, refining task assignments and fleet sizing. This closed loop turned design into a living model that consistently guided better, faster operating decisions.
Dashboards Operators Actually Use
Instead of vanity charts, operations built role-specific views: planners saw wave health, pickers saw priorities, and maintenance watched battery and sensor alerts. Clear thresholds triggered standardized responses, reducing downtime and helping new team members succeed confidently within their first few shifts.
Continuous Improvement Cadence
Weekly kaizen sessions reviewed exceptions, heat maps, and near-misses. Small tweaks—tweaked slotting, rebalanced pick zones, refined robot priorities—stacked meaningful gains over time. Sharing these wins publicly reinforced a culture where everyone, from IT to receiving, contributed actively to automation success.
From Chaos to Flow: Anecdotes You Can Feel
A regional 3PL dreaded late Friday drops. After automation, AMRs pre-staged high-velocity SKUs, and exception lanes handled specials without drama. The team left on time, customers received tracking earlier, and Mondays stopped feeling like recovery missions from an exhausting weekend backlog.